Global Cold Supply Chain Overview (2018–2025)
Trends, Challenges, and Technological Drivers of Transformation | CRYOX AI: Smarter • Greener • Resilient Cold Chains
Executive Summary
Between 2018 and 2025, the global cold supply chain has undergone major transformations, driven by growing demand in pharmaceuticals, agrifood, and e-commerce logistics. The industry, valued at $160B in 2018, expanded to over $320B by 2024 and is projected to exceed $860B by 2032. Despite this growth, structural inefficiencies persist.
This white paper highlights market dynamics, challenges, and the role of advanced technologies in shaping a sustainable cold chain ecosystem.
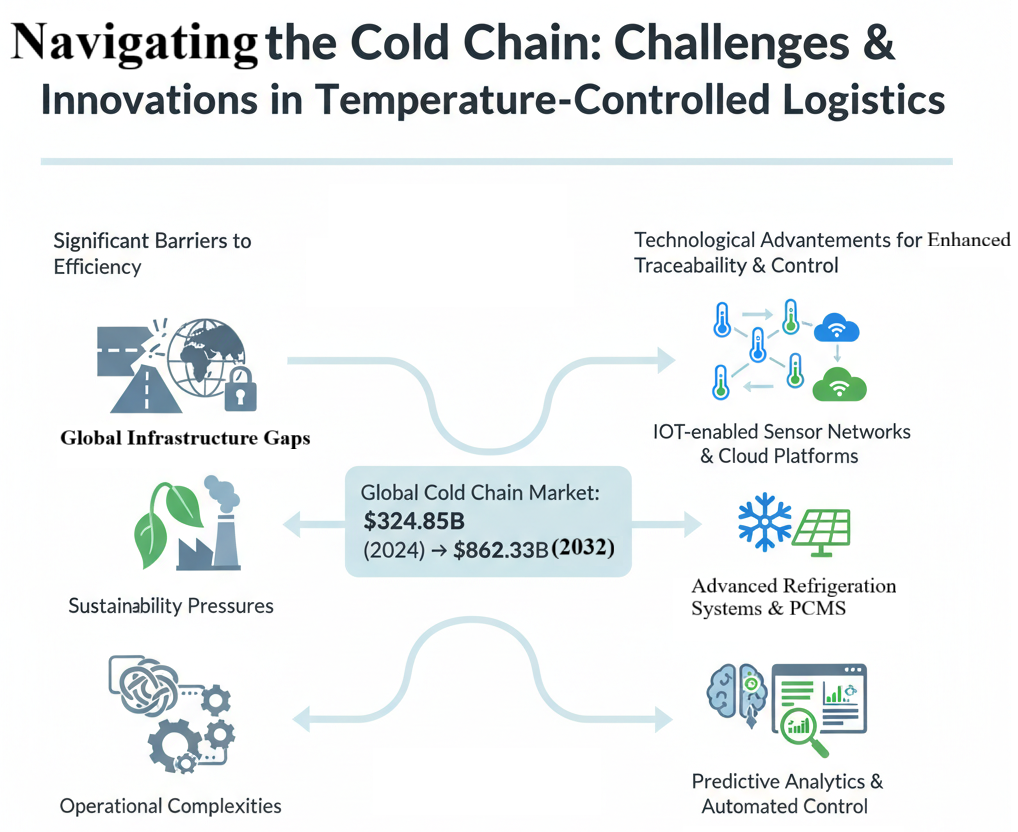
Figure 1. Critical applications and impact of global cold supply chains.
Global Market Evolution (2018–2025)
The period 2018–2025 marked significant cold chain expansion, particularly in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa. Drivers include rising global trade in perishable goods, COVID-19 vaccine distribution, and rapid growth in e-commerce grocery delivery. Investments in cold storage, reefer fleets, and last-mile delivery intensified, but infrastructure gaps remain stark in developing economies.
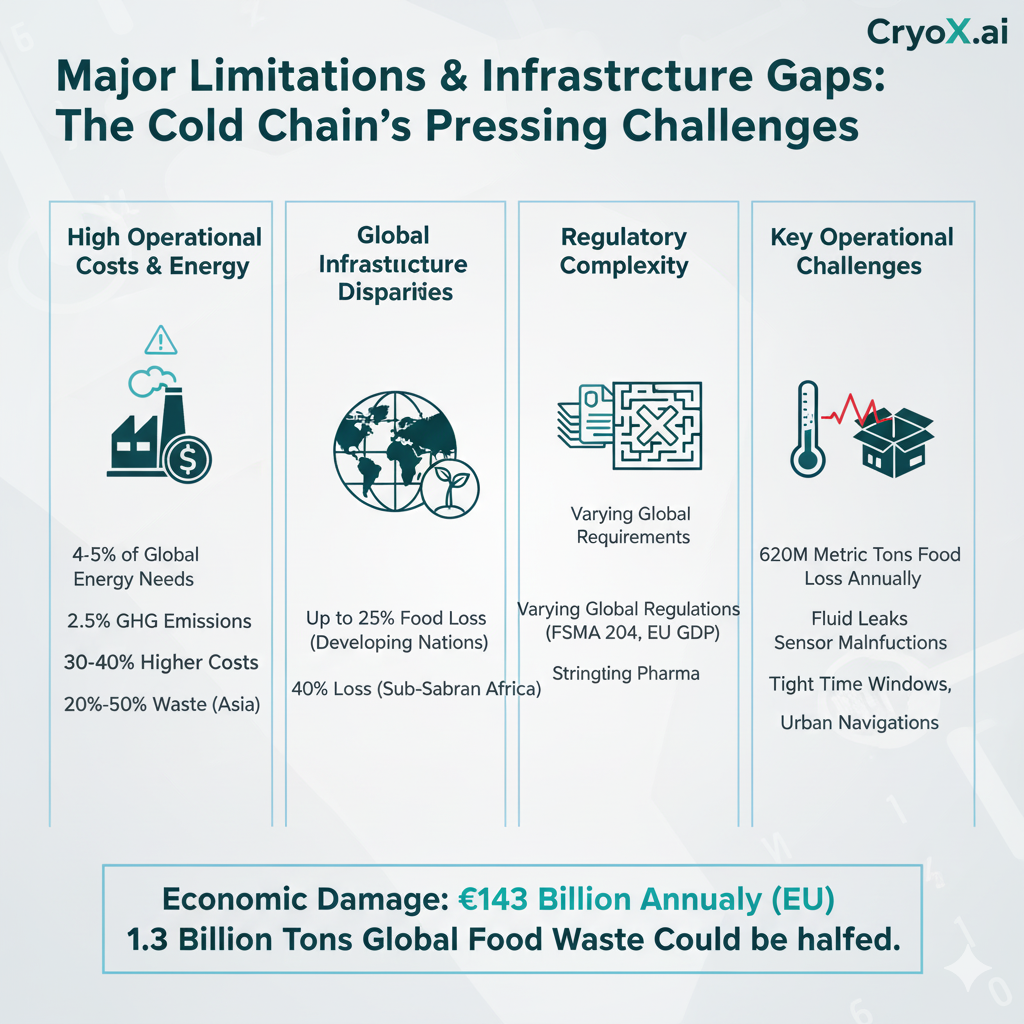
Figure 2. Historical evolution of the cold chain sector (2018–2025).
Key Challenges
- High operational costs and energy consumption — cold chains consume 4–5% of global energy.
- Infrastructure disparities — 25–40% of perishables are lost in developing countries.
- Regulatory complexity — varying standards in pharmaceuticals, agrifood, and logistics.
- Last-mile delivery risks — urban congestion and multiple transfer points raise spoilage risks.
The economic damage in the EU alone is estimated at €143 Billion Annually, with the potential to halve the 1.3 Billion Tons of Global Food Waste.
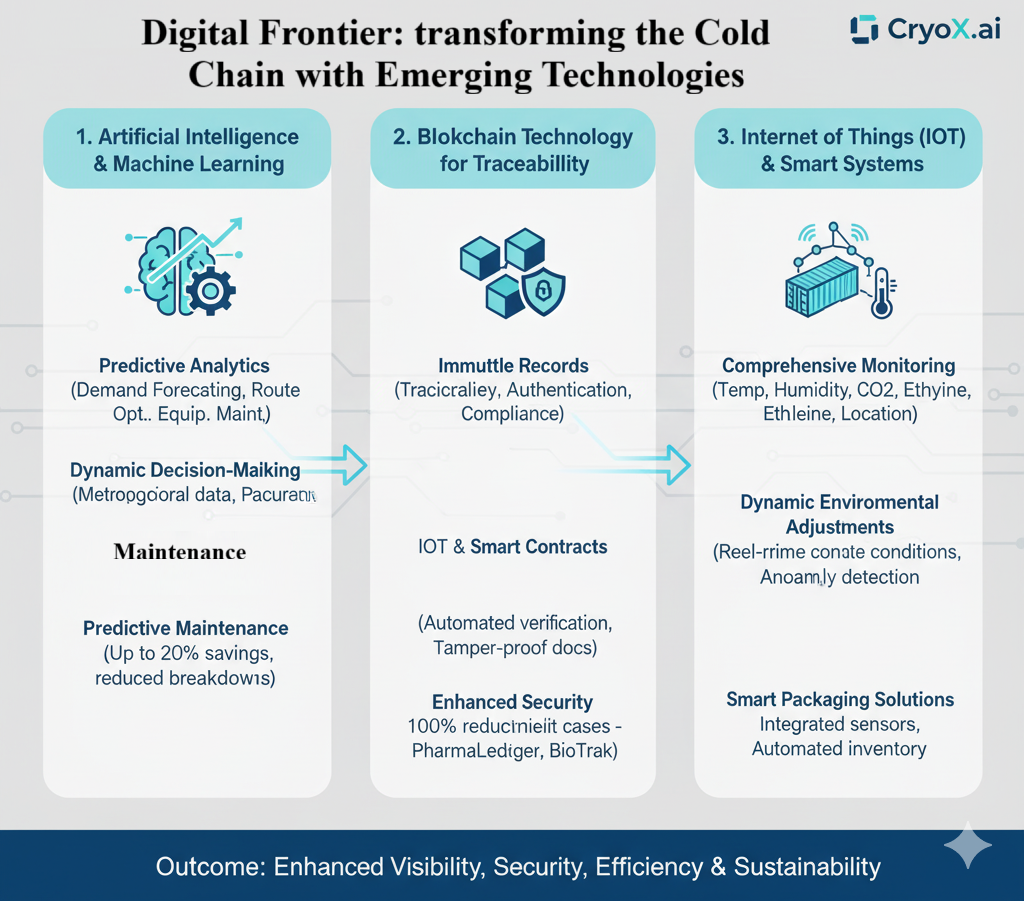
Figure 3. Digital Frontiers: Transforming the Cold Chain with Emerging Technologies (AI, Blockchain, IoT).
IV. Technology Drivers (2018–2025)
Technological innovation between 2018 and 2025 has reshaped cold chain operations:
- IoT sensors & cloud platforms expanded monitoring of temperature, humidity, and location.
- AI & predictive analytics improved demand forecasting and equipment maintenance.
- Blockchain pilots in pharma and food improved traceability and compliance.
- Green refrigeration and natural refrigerants emerged as sustainability priorities.

Figure 4. Horizon Scan: Future Trends Shaping the Cold Chain (Autonomous Vehicles, Digital Twins, Green Computing).
V. Key Insights and Catalyst for Change
Case studies illustrate the shift:
- Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccine distribution highlighted Cold Supply Chain (CSC) weaknesses and digital twin use.
- Maersk and DHL invested in smart reefer fleets and AI-powered logistics.
- Regulatory frameworks such as FSMA Rule 204 and EU GDP became global reference points.
Catalyst for Change: The Transformative Impact of Cold Chain Technologies
The convergence of digital technologies leads to three key impact areas:
- Operational Transformation: Increased automation, visibility, and predictive capabilities.
- Sustainability & Efficiency Gains: Potential 41% reduction in food waste GHG emissions and $150 Billion in annual savings for developing countries.
- Global Development Impact: Reduced food losses and improved access to medicines via mobile cold storage and IoT for remote areas.
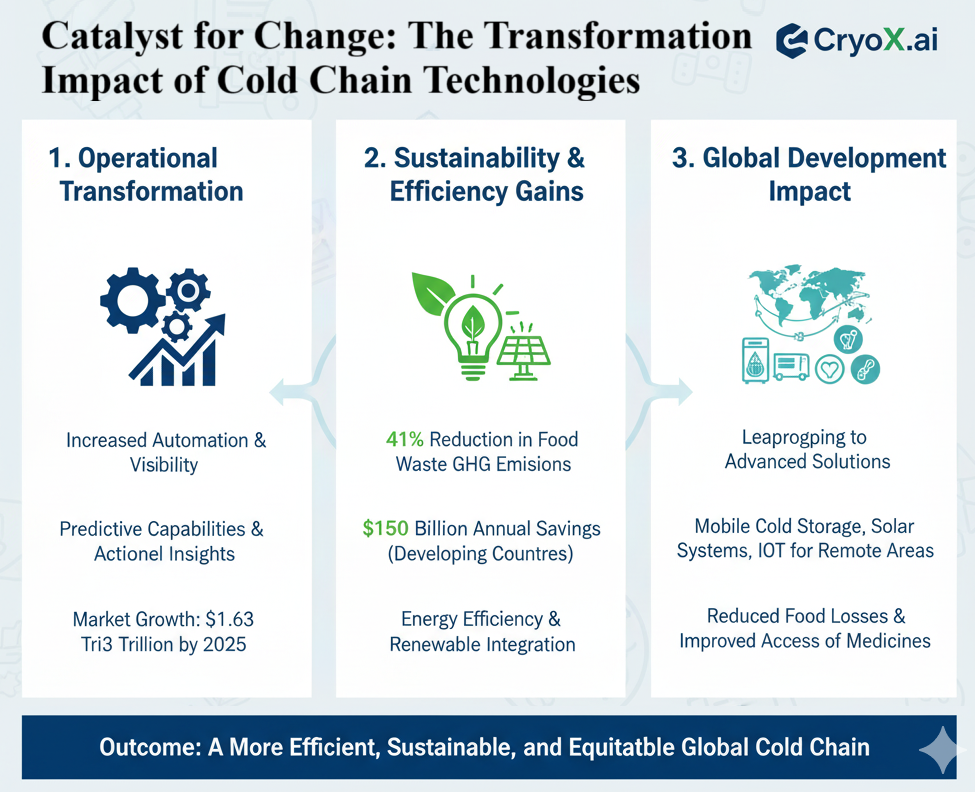
Figure 5. Economic and public health impacts of cold chain systems.
VI. Conclusion
The global cold supply chain has doubled in value from 2018 to 2025, but inefficiencies and sustainability gaps persist. Emerging technologies offer clear pathways to resilience and efficiency. As the sector moves toward 2030, success will depend on coordinated investment in infrastructure, digital integration, and sustainable practices.
Learn How Cryox AI Delivers Measurable ROI
Cryox AI is leading the transformation. Contact us to schedule a discussion on leveraging Neuromorphic Edge AI for your cold chain operations.
Connect with Our Experts